Since Augmented Reality (AR) had its beginnings in the gaming world in the 1960s, it evolved to be a ubiquitous technology both in private and commercial life. As millions want to utilize the interactive experience by blending digital elements and a computerized real-life environment, the AR market is booming: It’s forecast to jump to USD 72.7 billion by 2024, from USD 10.7 billion in 2019.
As people and businesses are willing to spend billions on AR technologies, they want to optimize their resources and make the most out of the innovations available to them. Hence, they might be asking: What are the pros and cons of smartphones vs. smart glasses for AR? Which augments reality better?
Pairing AR with Smartphones or Smart Glasses
AR smart glasses are wearable and transparent devices that augment the reality within the scene of the user’s viewpoint. AR smart lenses or virtual retinal displays, two emerging AR technologies that are yet to go mainstream, also fall under this category. Wearing these glasses allows the user to see the real world augmented with virtual content or information in their surroundings.
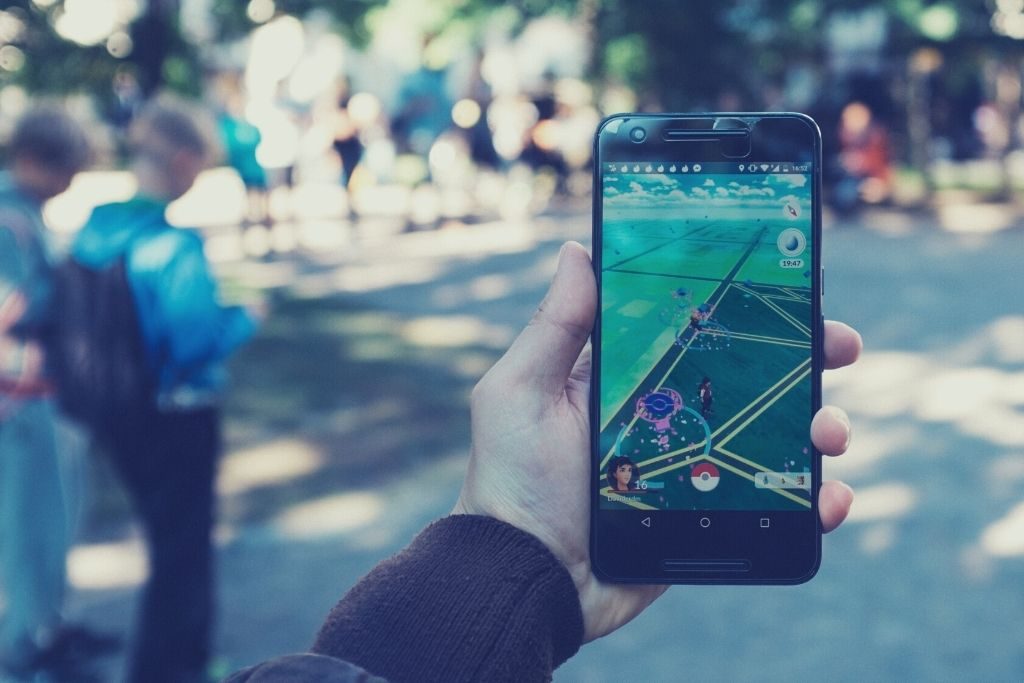
On the other hand, AR-enabled smartphones or tablets tap into the device’s camera to augment reality. Applications such as Snapchat filters or the mobile game Pokemon GO are omnipresent examples of this.
Pros and Cons of Smartphones vs. Smart Glasses in AR

“The predominant difference between doing augmented reality with a tablet or phone versus smart glasses is you’re truly mobile” if you have the glasses on, says Brian Ballard, CEO of Upskill, an enterprise app platform for wearables and AR.
[Say] you’re a car mechanic. [The smart glasses] know that you’re working under the hood of a car because they’ve been tasked to follow your steps … That information is right there keeping pace with you, rather than you having to flip through the pages of a manual.
Brian Ballard, CEO Upskill
Hence, especially in an industrial environment, augmenting reality via smart glasses has distinct advantages. It has proven benefits to improve workplace safety, supercharge project visualization, and enhance productivity.
However, smart glasses are still emerging technologies with imperfections. Many tech enthusiasts considered the early models such as the pioneering Google Glass — which was unveiled in 2012 — as failures.
Since then, there have been considerable improvements. In 2019, the first models that can be used in industrial settings started to emerge. Nevertheless, the cost of the AR glasses currently in the market are still substantial.
Smartphones: Cheaper and Accessible, But With Limiting Features

On the other hand, smartphones are still cheaper and are now an accessible and ingrained habit for millions. “We’re using the phones right now. Everyone uses their phones. We’re not forcing people to do things that are dramatically different from what they currently do,” says Jonathan Chizick, former COO of the game developer Candy Lab.
Smartphones are still a significant driver of the AR growth due to their convenience. Nevertheless, they have considerable limitations: While using them, AR environment is limited by the size of the smartphone screen, unlike the 360-degree field of view glasses can offer. Likewise, the users always have to hold the smartphone with one hand, which might hinder their productivity.
That said, especially in non-industrial settings, there are many ways AR-enabled smartphones can add value outside gaming, such as receiving customer support, learning a new skill, or navigation.
Final Verdict on Smartphones vs. Smart Glasses
All in all, there’s no doubt that AR can enhance people’s daily lives and the day-to-day operation of companies — whether it’s used through a smartphone or a smart glass. As these technologies are still evolving at a rapid pace, both options will likely keep substantially improving.
In the meantime, analyzing their needs and budgets, while understanding the pros and cons of smartphones and of smart glasses in AR, people can make the informed and right decision.