The Industrial Revolution brought coal-powered factories and dense urban living, spewing air pollutants like soot and chemicals, making buildings suffer from grime, dampness, and poor indoor air quality – while introducing a devastating environmental toll. Since then, the construction industry has been a major contributor to environmental pollution and resource depletion.
However, in recent years, there has been a growing shift towards green building practices and sustainable architecture. Architects and builders are rethinking their approach, prioritizing sustainability and minimizing the footprint of their creations.
As technology advances and environmental awareness grows, we can expect even more innovative and sustainable designs to emerge, shaping a future where buildings are not just functional spaces but responsible members of our environment.
Hereafter are five exciting trends shaping modern environmental architecture.
1. Biomimicry – Where Nature is the Blueprint

Mother Nature, the ultimate innovator, has been perfecting solutions for efficiency and resilience for millions of years. Biomimicry, a fascinating field, learns from these ingenious designs and translates them into remarkable feats of sustainable architecture.
This approach can help architects to create buildings that stay cool naturally, inspired by the intricate ventilation systems of termite mounds. Or self-cleaning facades, mimicking the water-repellent surface of the lotus flower, reducing maintenance and harmful chemicals.
Even the incredible strength and flexibility of spider silk holds potential for new, sustainable building materials. Biomimicry is pushing the boundaries of architecture, drawing inspiration from nature to create greener, more efficient structures for the future.
2. Modular Construction – Blocking for Efficiency

Traditional construction can be wasteful and resource-intensive, generating mountains of material scraps and consuming significant energy. Enter modular construction, a greener alternative where buildings come prefabricated, assembled from sections built in controlled, off-site environments.
Modular construction delivers several advantages for environmental architecture: Reduced waste through precise manufacturing, improved efficiency with faster construction times and lower emissions, and remarkable flexibility in expanding, reconfiguring, or even relocating modular buildings to adapt to changing needs.
It’s like building with Legos, but on a grander, greener scale.
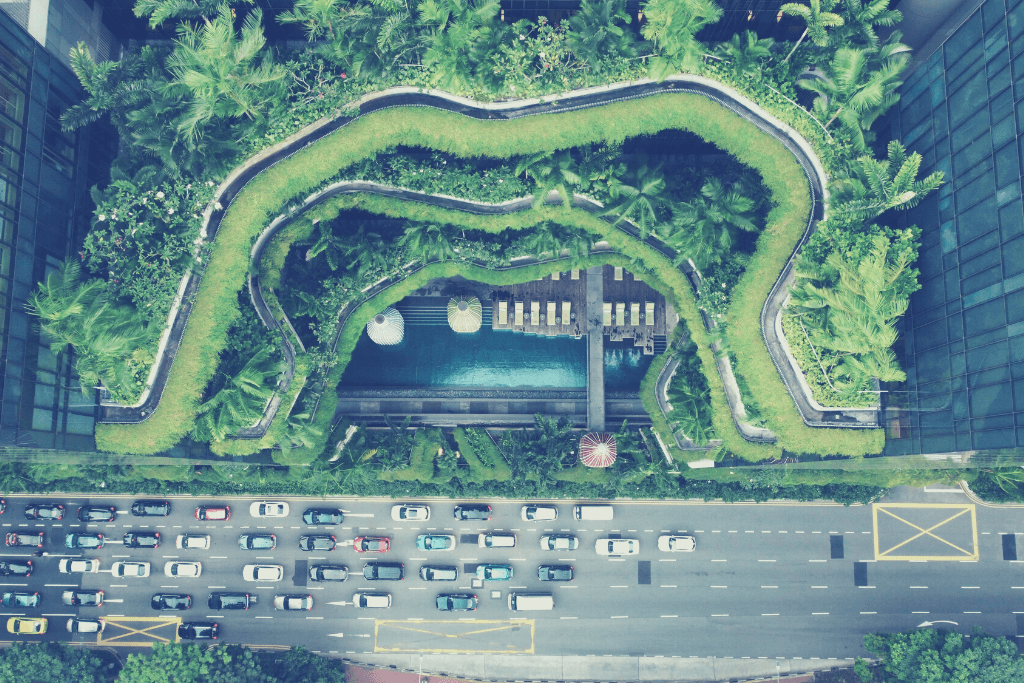
3. Living Architecture – Taking a Deep Breath with Nature
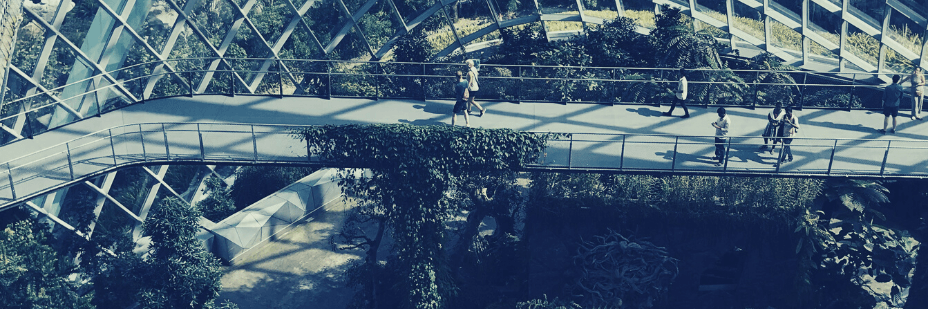
Imagine buildings more than just concrete shells, but thriving ecosystems that breathe with nature. Living architecture embraces this vision, weaving elements like green roofs, vertical gardens, and natural ventilation systems into its very fabric.
This integration unlocks a bounty of benefits: Plants act as nature’s own air filters, cleansing the air within and creating healthier spaces. Green roofs and clever ventilation systems become partners in temperature regulation, reducing reliance on energy-hungry HVAC systems.
Most importantly, living architecture connects us to nature, studies showing that its presence reduces stress, sharpens minds, and fosters a sense of well-being for those who dwell within. It’s a way to blur the lines between inside and outside, building structures that breathe and thrive alongside us.
4. Material Revolution – Bamboos over Bricks

The construction industry is witnessing a material revolution, where sustainability and performance go hand in hand. Renewable resources like bamboo, straw, and even mycelium are finding their way into building blocks, offering a greener alternative to the concrete and steel giants of the past.
These bio-based materials are not just eco-friendly; they bring unique aesthetics and properties to the table. But the green wave doesn’t stop there. We’re also seeing innovation in the realm of recycled materials, where waste plastic and glass are finding new life as building components, reducing environmental impact and creating buildings that are both resource-efficient and stunningly unique.
Add the smart materials into the mix – the ones that change color to regulate temperature or even generate energy from sunlight. These futuristic materials push the boundaries of what buildings can do, paving the way for structures that are not just passive shelters, but active participants in a sustainable future.
5. Tech-powered Sustainability – The Ultimate Green “Hack”
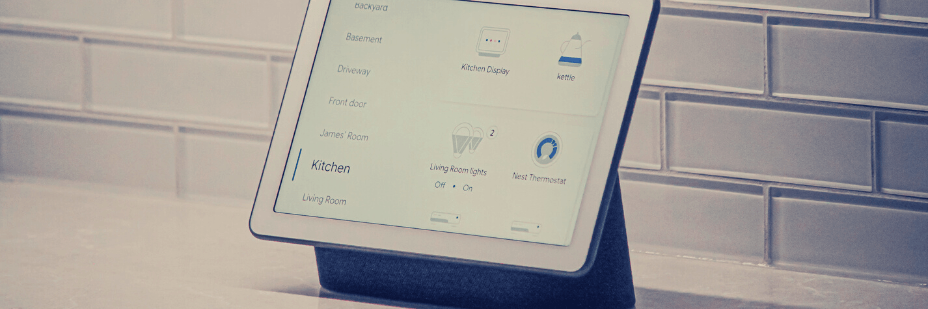
Technology isn’t just a guest at the green building party, it’s the host, spinning sustainability into reality.
Tools like BIM software allow architects and engineers build virtual models, tweaking for optimal efficiency and spotting flaws before the first brick is laid. Gone are the days of fossil fuel guzzlers – buildings are sprouting solar panels like sunflowers, catching the sun’s rays and breathing life into cleaner energy grids.
And then there are the smart building systems, the tireless assistants whispering to lights, heaters, and vents, ensuring maximum comfort with minimal environmental impact. It’s like having a building on autopilot, constantly adjusting for the perfect balance of green living and modern convenience.
With technology as our guide, buildings are evolving from static structures to dynamic partners in a sustainable future.







